How Do You Know a 1 Yo Has Ear Infection
Ear infections are very mutual in small children. About infections get better speedily and are not commonly serious. The two types of ear infections oftentimes seen in children are centre ear infections (otitis media) and outer ear infections (otitis externa). Most ear infections involve the middle ear.
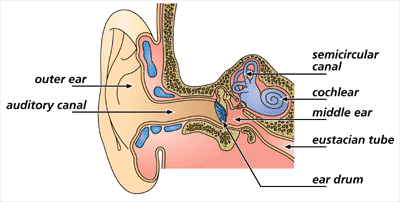
Every fourth dimension a centre ear infection happens, fluid collects behind the ear drum. This fluid unremarkably slowly clears past itself, simply children who get frequent infections may have fluid stay behind the eardrum for longer. This is chosen glue ear. Glue ear may terminal for many weeks or months, making it harder for your child to hear. Occasionally, glue ear can temporarily affect language evolution.
What causes ear infections?
Babies and young children get more centre ear infections than older children because they accept smaller tubes (called the Eustachian tubes) that connect the middle ear to the throat. When your child has a common cold, germs from the pharynx can travel upwards to the middle ear and cause an infection. Infections develop more easily in smaller tubes and it's not uncommon for small children to have lots of ear infections in one year, sometimes as often as once every month.
Outer ear infections are usually due to excess moisture in the canal, for example later on swimming. They can also exist acquired by damage to the canal (e.thou. from scratching or cleaning with earbuds).
Signs and symptoms of ear infections
Babies and children may have ear pain with both middle and outer ear infections. This pain can cause irritability. Your child may also have symptoms of a cold (e.g. runny olfactory organ, sore throat).
Heart ear infections (otitis media)
- As fluid collects behind the eardrum, it causes the drum to bulge, resulting in intense pain. Occasionally, the eardrum will bulge so much that information technology tears (this is called a burst eardrum), and you lot will run into a thick xanthous discharge come up from the ear. When this happens, children often all of a sudden feel meliorate, as the bulging has stopped. A burst eardrum normally heals without treatment.
- Children with middle ear infections oft have a fever – sometimes a fever will be the only symptom of a heart ear infection.
Outer ear infections (otitis externa)
- There can be discharge from the ear, or your kid might complain of a feeling of fullness in their ear.
- The ear may exist red and swollen. The redness may spread beyond the ear.
- The ear may be painful to bear upon and motility.
- Your child may take a fever.
Glue ear
Gum ear is not an infection, but usually follows one or more middle ear infections. Signs and symptoms of glue ear can include:
- problems hearing – children may want to have things repeated, talk loudly or have the television upwardly loud. Parents or teachers may notice this, particularly in noisy places such equally classrooms. In smaller children, hearing difficulties may delay or stall their language evolution.
- some pressure or hurting in the ear
- irritability or problems sleeping
- bug with remainder.
When to see a medico
If you think your child may have an ear infection, take them to see the GP.
A middle ear infection may spread to the firm, bony surface area behind the ear. Yous should visit your GP or local emergency department if there is redness, swelling or pain in this area.
If your child has frequent ear infections or their hearing appears to exist affected by glue ear, they should have their hearing tested by a hearing specialist (an audiologist). Your GP may too refer them to encounter a paediatrician or an ear, olfactory organ and throat (ENT) specialist.
Treatment
- Antibiotics are not oft used to treat centre ear infections, as they are often acquired past a virus. Antibiotics do not treat viruses. In very young or very unwell children, the GP may prescribe a short course of antibiotics if there'south risk of bacterial infection.
- Outer ear infections e'er demand treatment with antibody drops.
Gum ear
- If your child is non bothered by the gum ear, no handling is needed. It usually goes away past itself over time.
- Sometimes antibiotics are prescribed to kill whatsoever germs left in the centre ear, and this may help the fluid to clear.
- If the gum ear yet persists and is affecting your kid's hearing over many months, your doctor or ENT specialist may propose surgery. This is a quick operation during which small tubes (chosen grommets) are put into your child'south ear. These tubes help fluid drain from the eye ear.
Care at habitation
- If your child is in pain, you can give them pain relief, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen. See our fact canvass Pain relief for children.
- If your kid'south doctor prescribes ear drops, have your child lie down with the affected ear facing the ceiling. Put the drops in and continue your child in the aforementioned position for a few minutes, to let the drops to be absorbed (or place a cotton wool ball in the ear to keep the drops in the canal).
- Children with an outer ear infection should avoid swimming for one week to allow the infection to heal.
- If your kid has hearing troubles that don't amend in the weeks following a centre ear infection, or continues to be irritable, get back to the GP as your child may have glue ear.
- Your child may sleep better at night if they are propped up on two or more pillows (only practise this if your child is old plenty to use pillows).
- Don't allow anyone to smoke in the home or effectually your kid. Cigarette smoke has been shown to stop fluids from being able to drain from the eardrum.
- Most children outgrow heart ear problems (including glue ear), and have perfect and undamaged ears with normal hearing when they get older.
Key points to recollect
- It's common for small-scale children to accept several ear infections in one year, equally often as one time every month.
- Antibiotics are non often needed for heart ear infections, but outer ear infections are treated with antibiotic ear drops.
- Mucilage ear is caused by fluid that collects behind the eardrum, in the heart ear. It normally clears on its own with no treatment, but sometimes requires surgery to insert grommets for drainage.
- Hearing and speech development can exist affected if mucilage ear is persistent.
For more than information
- Kids Health Info fact sheet: Fever in children
- Kids Wellness Info fact sheet: Pain relief for children
- Kids Wellness Info fact canvass: Tonsillitis
- Better Wellness Channel: Ear infections
Common questions our doctors are asked
Can my child go swimming during an ear infection?
If your kid has an outer ear infection, expect until one week after handling to give the ear time to heal earlier letting your child swim. For centre ear infections and glue ear, swimming is OK simply should be avoided if the ear pulsate is perforated. Talk over this with your GP or specialist.
If my child has speech problems acquired by mucilage ear, will surgery assist their voice communication better?
If language delay is caused by difficulty hearing from glue ear, so correcting the mucilage ear often results in rapid improvements in language. Most children catch upward quickly with their peers and the delay is completely corrected.
My child is in a lot of pain with his ear infection. Can I give Painstop?
Painstop is ordinarily not required, and is at present only available by prescription. It contains codeine, which may crusade nausea or constipation in children. Paracetamol and ibuprofen can exist used safely.
Volition my kid grow out of their ear infections?
As children abound, the tubes in their ears (called the Eustachian tubes) as well grow. This is commonly associated with fewer - and less severe - ear infections as the kid grows. Every bit they get older, children tend to have fewer colds, and this means they volition likewise have fewer ear infections.
Should I make clean my child'due south ears to prevent a build-up of wax?
No. There is no need to remove the wax in a child's ears. The body is able to do this by itself. Big clumps of wax that are visible at the opening of the ear canal tin can be removed, simply earbuds should not exist used in children.
Developed by The Regal Children's Hospital General Medicine, Emergency and Otolaryngology departments. We admit the input of RCH consumers and carers.
Reviewed March 2018.
Kids Health Info is supported by The Majestic Children's Hospital Foundation. To donate, visit world wide web.rchfoundation.org.au.
Source: https://www.rch.org.au/kidsinfo/fact_sheets/Ear_infections_and_Otitis_media/
0 Response to "How Do You Know a 1 Yo Has Ear Infection"
Post a Comment